What is VPC Peering?
A networking link that allows you to route traffic between two VPCs using private IPv4 or IPv6 addresses is called a VPC peering connection.
Instances in either VPC can communicate with each other as if they are within the same network.
You can create a VPC peering connection between your own VPCs, or with a VPC in another AWS account.The VPCs can be in different Regions (also known as an inter-Region VPC peering connection).
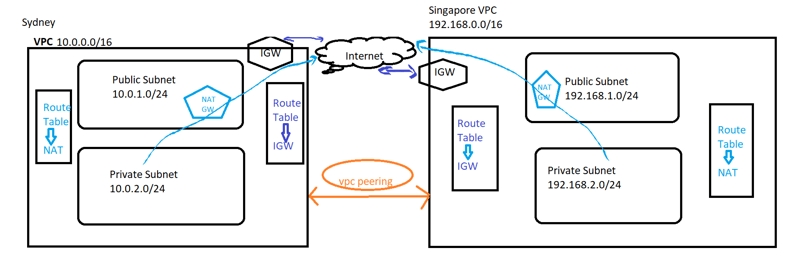
Here are some key points about VPC peering
- Interconnection: VPC peering allows VPC instances to communicate with each other using private IP addresses. This communication takes place over the internal network of the cloud provider, avoiding exposure to the public internet.
- Isolation: Despite the interconnectedness provided by VPC peering, each VPC retains its own network configuration, security settings, and control over resources. This means that VPCs can communicate securely while remaining isolated from each other’s configurations.
- Transitive Peering: Some cloud providers support transitive peering, which allows VPCs to establish peering connections with other VPCs indirectly. For example, if VPC A is peered with VPC B, and VPC B is peered with VPC C, then VPC A can communicate with VPC C through VPC B.
- Limitations: There might be limitations on VPC peering configurations imposed by the cloud provider, such as restrictions on overlapping IP address ranges or limitations on the number of peering connections allowed per VPC.
- Use Cases: VPC peering is commonly used for scenarios where different applications or services hosted in separate VPCs need to communicate with each other privately. This can include scenarios like microservices architectures, multi-tier applications, or separating development, testing, and production environments.
The cost of a VPC peering connection
Establishing a VPC peering connection is free of cost. When a VPC Peering connection remains inside an Availability Zone (AZ), all data transfer is free. Transfer of data across Availability Zones and Regions via VPC Peering connections is subject to costs.
Want to learn Hands-on on Application load balancer ?
Let’s check out practically
- Step 1: Create two VPCs in your AWS Account
- Creating VPC in Sydney Region

- Step 2: Create Public and Private subnets



- Step 3: Create Internet Gateway

Attach to VPC after creating internet gateway


- Step 4: Once Internet gateway is attached to VPC, Create Route Table

After creating Route Table, edit the subnet associations and add the routes


Public subnet is associated and now add the route to IGW

- Step 5: Create NAT Gateway and add private route table
- NAT Gateway must be placed on public subnet and also allocate Elastic IP

Now create private route table, edit subnet associations and add route to NAT GW



- Resource Map

- Step 6: Launch Public and Private Servers (Using Ec2 )

- Step 7: Similarly as shown above create VPC, IGW, Public Route Table, NAT GW, Private Route table in Singapore region
- Step 8: Also Create Public and Private Servers in Singapore Region( Using Ec2)
- Step 9: Final step is to create VPC Peering Link
- Initiate peering from any one side( Singapore Region), and accept the peering in another side (Sydney Region)


Go to Sydney Region and accept peering request

VPC peering is successfully created and active



Pingback: Setting up Application Load Balancer in AWS: Hands-On - wordwyzz